Photosynthesis: Nature's Energy Production
- Sylvia Rose

- Feb 8, 2025
- 3 min read
Photosynthesis supports life on Earth. In this process, plants turn sunlight into sugars for energy and provide much-needed oxygen to animals, fungi and microbes inhabiting nearly every niche on the planet.

About Photosynthesis
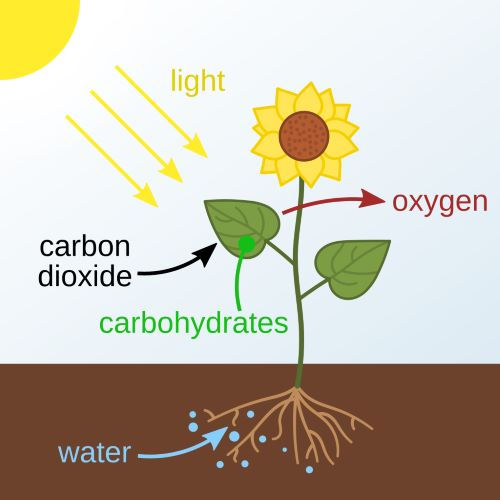
Photosynthesis happens in green plants, algae and some bacteria. The process converts solar light energy into chemical energy. Carbon dioxide and water, in the presence of light energy, yield glucose and oxygen.
Without oxygen life ceases, except for a few anaerobic chemosynthetic microbes who start new cultures. Simple sugar glucose, a carbohydrate, is food for plants and ultimately many organisms including humans.
It forms the base of food chains, delivering solar energy as glucose and polysaccharides like starch to herbivores, omnivores and carnivores. Glucose can form multiple compounds from maltose to cellulose.
Chloroplasts
Chloroplasts are the organelles where photosynthesis takes place in plant cells. They contain chlorophyll, the green pigment able to capture sunlight. Inside chloroplasts, at an even more microscopic level, thylakoids are arranged in stacks called grana, surrounded by fluid called stroma.
Thylakoids are crucial for absorbing sunlight, while the stroma is vital for glucose synthesis. This diversity helps chloroplasts efficiently convert sunlight to chemical energy.

The Two Main Stages of Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis proceeds in two main stages: the light-dependent reactions and the light-independent reactions, often known as the Calvin Cycle.
Light-Dependent Reactions
These reactions occur in the thylakoid membranes of chloroplasts. When chlorophyll captures sunlight, it excites electrons. This triggers a chain of reactions producing ATP (adenosine triphosphate) and NADPH (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate), both energy carriers.
During this stage, water molecules are split, releasing oxygen as a byproduct. When exposed to bright sunlight, photosynthesizing plants can generate up to 18 ATP molecules per 6 carbon dioxide molecules processed. This energy fuels the next phase of photosynthesis.

The Calvin Cycle
The Calvin Cycle occurs in the stroma, where ATP and NADPH from the light-dependent reactions convert carbon dioxide into glucose. This stage involves carbon fixation, reduction, and regeneration.
Plants turn inorganic carbon in the atmosphere into organic carbohydrates during these phases. The Calvin Cycle doesn't need light directly; it's also known as light-independent reactions. It relies on energy created during the light-dependent reactions.

The Importance of Photosynthesis
Oxygen Production: It generates the oxygen necessary for aerobic creatures and thereby contributes to 21% of Earth's atmosphere.
Food Source: It's the base of the food chain system.
Climate Regulation: Photosynthetic organisms absorb vast amounts of carbon dioxide. This is essential to survival on Earth, potential climate regulation and activities like breathing.

Factors Affecting Photosynthesis
Light Intensity: Increased light generally raises photosynthesis rate until it reaches a saturation point.
Carbon Dioxide Concentration: Higher carbon dioxide levels can accelerate photosynthesis, as CO2 is a raw material. If more CO2 is present than the plants can handle, it remains in the environment.
Temperature: Each plant has an optimal temperature range for photosynthesis. Wheat grows best at 21° - 24° C (70° - 75° F). Plants such as maize, sugar cane and sorghum show adaptation to higher temperatures.
Water Availability: Water is a reactant in photosynthesis; droughts severely disrupt this process.

Non-Fiction Books:
Fiction Books:
READ: Lora Ley Adventures - Germanic Mythology Fiction Series
READ: Reiker For Hire - Victorian Detective Murder Mysteries


